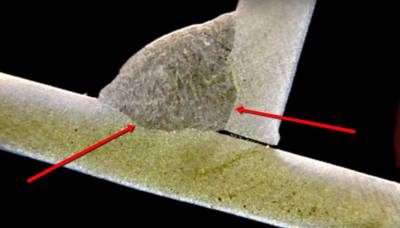
Can You Weld Aluminum With a Regular MIG Welder?

Can You Weld Aluminum With a Regular MIG Welder? Yes, but you must set your welder up correctly using the correct gas, wire, and liner. You’ll also want to keep the welding liner straight to avoid snapping the wire.
- Power source: To weld aluminum with a regular MIG welder, the machine must have a power source capable of producing a high-frequency output. This is necessary to create the necessary arc to start the weld.
- Wire feeder: The wire feeder on the MIG welder must be capable of providing the necessary wire feed rate and voltage to ensure a consistent, stable arc.
- Gas flow: A shielding gas suitable for welding aluminum must prevent oxidation and protect the weld from contamination. Argon is the most commonly used shielding gas for welding aluminum.
- Welding gun: A welding gun with a gas lens and collet must be used for aluminum welding. This will help to focus the gas flow and provide a consistent arc.
- Welding wire: A welding wire designed for aluminum welding must be used. The most common wire for welding aluminum is 4043.
- Technique: Welding aluminum requires a specific technique. It’s important to use short arc welding and maintain a close distance between the electrode and the workpiece.
It’s important to note that welding aluminum is more challenging than welding steel and requires more skill and specialized equipment. It’s advisable to consult with experts or professionals and practice scrap aluminum before welding aluminum in a production environment.
In this article, I will dive into these six areas when welding aluminum with a MIG welder and the best practices to make it work.

#1 What Type of Power Source Should You Use for Welding Aluminum
When welding aluminum with a MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welder, a specific power source is required to create a stable arc and achieve a high-quality weld. The following are some technical considerations when it comes to the power source:
- Inverter-based power source: Inverter-based power sources are preferred for welding aluminum, as they produce a high-frequency output necessary to create the arc and start the weld. This high-frequency output also helps to prevent the electrode from sticking to the workpiece.
- Welding range: The power source should have a wide welding range, allowing the welder to adjust the output voltage and current to suit the specific aluminum alloy and welded thickness.
- Stabilized welding voltage: The power source should have a stabilized welding voltage, which ensures a consistent arc and a stable weld pool.
- Constant current output: A constant current output is preferred for welding aluminum, as it allows the welder to maintain a consistent arc and a stable weld pool.
- Pulse welding capability: Some advanced power sources have a pulse welding capability, which helps weld aluminum in thin sections where a high heat input is undesirable.
- High open-circuit voltage: A high open-circuit voltage (OCV) is needed when welding aluminum, as it ensures a stable arc and prevents the electrode from sticking to the workpiece.
It’s important to note that welding aluminum requires specific settings and equipment. It’s essential to consult the welder’s manual and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for welding aluminum.
A power source unsuited for welding aluminum might not provide the necessary high-frequency output, welding range, or other features needed for welding aluminum.

#2 Wire Feeder
When welding aluminum with a MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welder, a specific type of wire feeder is required to ensure a consistent and stable wire feed. The following are some technical considerations when it comes to the wire feeder:
- Wire drive rolls: The wire drive roll should be made of a material resistant to wear and corrosion, such as Teflon, as the aluminum wire is softer than steel wire and can wear out the wire drive roll quickly.
- Wire feed speed: The wire feed speed should be adjustable, as different aluminum alloys and thicknesses require different feed speeds. A higher wire feed speed will provide a broader and more fluid weld puddle, while a lower wire feed speed will provide a narrower and more controlled weld puddle.
- Tension: The wire feeder should have a tension adjustment, as too much tension can cause the wire to break, while too little tension can cause the wire to bird nest or bunch up.
- Gun liner: A gun liner specific to aluminum welding should be used, as it helps to guide the wire and prevent it from getting jammed or tangled.
- Burnback control: Some wire feeders have a burnback control feature that allows the welder to set the distance between the contact tip and the workpiece, preventing the wire from sticking to the workpiece once the trigger is released.
- Wire size: The wire feeder should be able to handle the specific wire size of the aluminum wire being used.
It’s important to note that the wire feeder plays an essential role in aluminum welding. Therefore, it’s important to use a wire feeder specifically designed for aluminum welding and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for adjusting and maintaining the wire feeder.
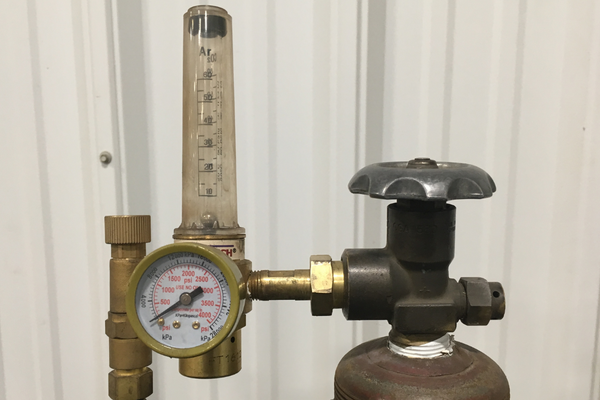
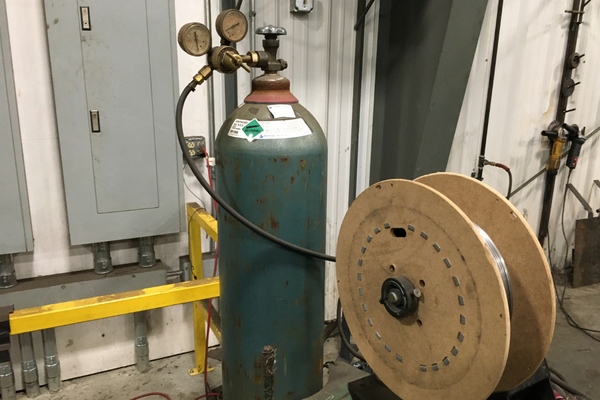
#3 What Kind of Gas Do You Use for MIG Welding Aluminum
The most commonly used gas for welding aluminum with a MIG welder is a mixture of argon and helium, known as “Ar/He.
This type of gas mixture is preferred due to its high thermal conductivity and low reactivity, which helps to prevent oxidation and promote a smooth, stable arc.
Additionally, the mixture’s helium component can help increase the weld’s penetration and width, resulting in a stronger, more durable bond.
Other gases that can be used for aluminum welding include pure argon or argon-helium blends, which are less commonly used due to their higher cost and lower performance.
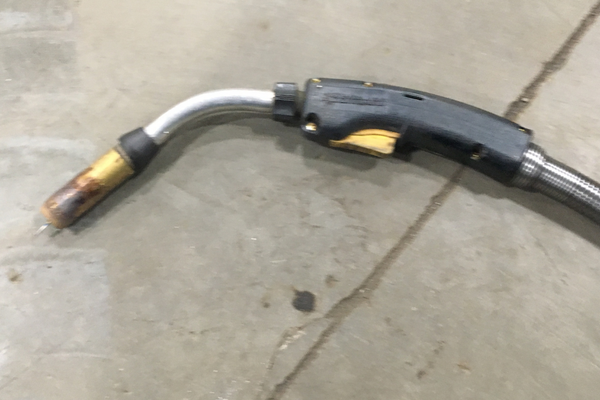

#4 What Kind of Welding Gun Do You Use for MIG Welding Aluminum
When welding aluminum with a MIG welder, it is recommended to use a gun specifically designed for aluminum welding. These guns typically have a larger diameter contact tip and a smaller gas lens to accommodate the different properties of aluminum wire.
Additionally, they may have a higher amperage rating and a different drive roll configuration to handle the softer and more malleable aluminum wire.
The gun should also have a liner made of Teflon or other high-temperature materials, as aluminum welding generates more heat than steel welding.
The gun should also be made of aluminum or other non-ferrous metals to prevent contamination of the weld by iron. The gun should have a push-pull mechanism to feed the wire more smoothly and consistently.
Additionally, it is important to ensure that the gun is equipped with a gas diffuser that can provide a consistent and stable flow of the Ar/He gas mixture to the weld area, as well as a proper nozzle that can direct the gas to the optimal location for shielding the weld.
Overall, the gun should be designed for high-performance aluminum welding and equipped with the proper components to ensure a smooth and consistent weld.

#5 What Kind of Wire Do You Use for Mig Welding Aluminum
When welding aluminum with a MIG welder, it is recommended to use aluminum welding wire designed explicitly for MIG welding.
The most common type of aluminum welding wire is 4043 alloy, a general-purpose alloy that can be used for welding various aluminum alloys. The wire can be made with various thicknesses and diameters, the most common being .030 inches and .035 inches up to .045.
Another popular alloy is 5356 alloy, known for its high strength, good corrosion resistance, and good penetration. The wire of this alloy is also suitable for welding thicker aluminum alloys.
It is important to note that aluminum welding wire is softer and more malleable than steel wire, so using a drive roll and gun liner designed explicitly for aluminum wire is essential. Additionally, the wire should be stored in a dry place and kept free of oil and other contaminants.
Overall, the choice of welding wire will depend on the specific application, the thickness of the material, and the desired result. It is recommended to consult the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines when selecting the appropriate welding wire for your project.
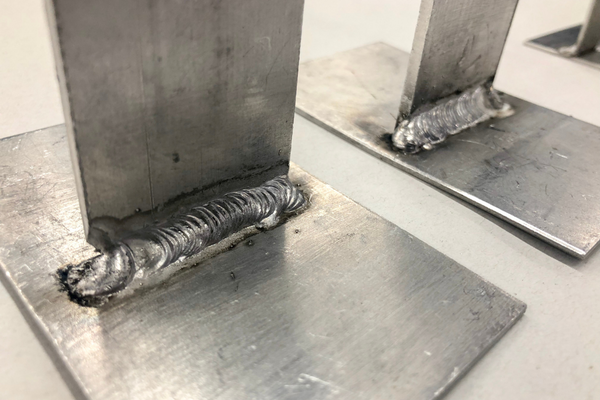

#6 Technique
When welding aluminum with a MIG welder, it is recommended to use the push technique, also known as “forehand welding.” This technique involves holding the gun at a 90-degree angle to the workpiece and pushing the gun forward toward the weld joint. This allows for better control over the weld pool and can help to reduce the risk of warping or distortion of the aluminum.
It is also essential to use a lower amperage setting when welding aluminum, as aluminum has a lower thermal conductivity than steel. This can help to prevent overheating and warping of the material. A higher travel speed is also important to prevent the weld from becoming too deep and wide.
Additionally, it is important to use the proper gas mixture, such as argon and helium (Ar/He), to shield the weld and prevent oxidation. Proper gas shielding is critical when welding aluminum as it prevents it from being exposed to air, which can cause oxidation and porosity, leading to weak and porous welds.
The proper welding technique for aluminum welding with a MIG welder involves using the push technique, lower amperage settings, a higher travel speed, and proper gas shielding to prevent oxidation. Using the correct wire and gun designed for aluminum welding is also essential.
Can You Weld Aluminum With a Regular MIG Welder?
Yes, you can weld aluminum with a regular MIG welder, but the aluminum wire is delicate and can break easily.
Hence, you need to keep your liner as straight as possible, use the right gas, and be careful not to get the heat too high, or you’ll have a lot of burn back and mess up a lot of tips.
To weld aluminum correctly, you’ll want a welder made for welding aluminum wire like this one.